√無料でダウンロード! mna-sf 794053-Mna sf pdf
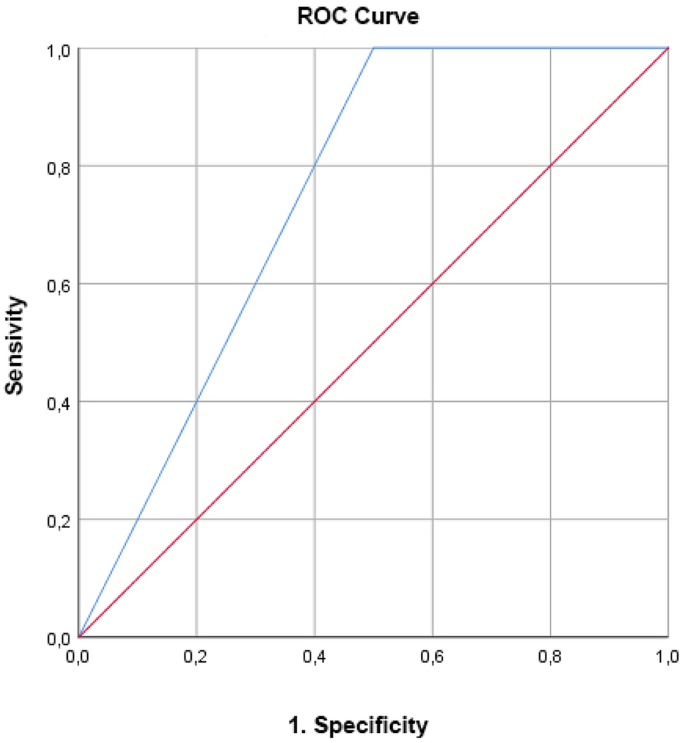
We analyzed the cutoff value on the MNALF score, MNASF score, and energyprotein intake for GLIM criteria–defined malnutrition severity with receiver operating characteristic analysis Results Malnutrition was present in 322%, 127%, and 131% of patients according to the GLIM criteria, MNALF, and MNASF, respectivelyAssessment, history, and MNASF results are consistent with adequate nutritional status Prepare equipment and supplies Explain to the person the purpose for nutritional assessment (or their power of attorney for personal care should the person not The MNASF is a simple and cheap tool widely used to assess nutritional status in elderly subjects It has been validated in numerous countries, including Poland 28 The diagnostics performance against the GLIM criteria for malnutrition was

A Review Of The Validity Of Malnutrition Screening Tools Used In Older Adults In Community And Healthcare Settings A Manuel Study Clinical Nutrition Espen
Mna sf pdf
Mna sf pdf-Nutritional Assessment (MNASF) J Geront 01;56A M Guigoz Y The MiniNutritional Assessment (MNA ®) Review of the Literature What does it tell us?The MNA®SF is a screening tool to help identify elderly patients who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition The User Guide will assist you in completing the MNA®SF accurately and consistently It explains each question and how to assign and interpret the score




Predictive Value Of Nutritional Risk Screening 02 And Mini Nutrition Cia
This tool (MNASF) is designed as a screening version of the original instrument Any health worker can use it, with minimal training required It has been demonstrated to be easy, rapid, and retains the validity of the original18item (Long Form MNA) and 6item (Short Form MNASF) questionnaire instrumentNutritional Assessment (MNASF) J Geront 01;56A M Guigoz Y The MiniNutritional Assessment (MNA
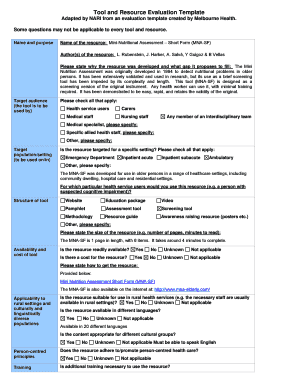
Engaged parties names, addresses and numbers etc Change the blanks with exclusive fillable areas Key Descriptions 2 variations Long Form MNA and Short Form MNASF;Current summary focuses upon the Long Form MNA;
A mini nutritional assessment short‐form (MNA‐SF) was confirmed overseas to identify malnutrition and predict clinical outcomes This study aimed to evaluate the MNA‐SF usefulness in Japanese small‐sized hospitalKaiser MJ, Bauer JM, Ramsch C, et al Validation of the Mini Nutritional Assessment ShortForm (MNA®SF) A practical tool for identificationTo validate a revision of the Mini Nutritional Assessment shortform (MNA(R)SF) against the full MNA, a standard tool for nutritional evaluation A literature search identified studies that used the MNA for nutritional screening in geriatric




Table 2 From Suitability Of The Short Form Mini Nutritional Assessment In Free Living Elderly People In The Northwest Of Spain Semantic Scholar




A Review Of The Validity Of Malnutrition Screening Tools Used In Older Adults In Community And Healthcare Settings A Manuel Study Clinical Nutrition Espen
A "MNASF template" was created on the electronic chart including assessment of each item with judgment criteria When information was entered into the template, a total score was automatically calculated and displayed Baseline cutoff values for the MNASF were 12–14 for "normal nutritional status",8–11 for "atResearch methodsandprocedures Nutritional screening tools, including the Nutritional Risk Screening 02 (NRS 02), the Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST) and the Short Form of Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNASF), were applied to 255 patients with gastrointestinal cancer We compared the diagnostic values of these tools for malnutrition, using the new ESPEN The MNASF allows quick screening to determinea persons risk of malnutrition (07) Early detection of malnutrition is important to allow targeted nutritional intervention and shouldbe a key component of the geriatric assessment The MNA, as a twostep procedure (screening with theMNASF followed by assessment, if needed, by the full MNA), is



Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mna Guide English Pdf




Uso Del Mini Nutritional Assessment Como Herramienta De Cribaje Nutricional En La Poblacion Mayor De 65 Anos En El Ambito Hospitalario Conveniencia Y Factibilidad
J Nutr Health Aging 06;The MNASF was revised in 09 so that a 'malnourished' category could be identified in addition to 'normal nutritional status' and 'at risk of malnutrition' (12) The Rapid Screen, developed in South Australia, comprises two items, body mass index and weight loss, and has been validated for adults aged over 65 years (4)When the MNASF indicates malnutrition risk, the nurse should proceed with part 2 (questions G through R), and both the screening score and the malnutrition indicator score should be documented When the total score indicates the risk of malnutrition or malnutrition itself, the primary care provider and the dietitian should be notified




Short Form Nestle Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna C Nestle 1994 Download Scientific Diagram



Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf Fill Online Printable Fillable Blank Pdffiller
Assessment® (MNASF) could be improved to enhance The rate of treatment response was significantly higher in applicability and facilitated implementation into geriatric patients with low compared to high risk, 652% and 275%, care respectively (p = 0005)The MNA®SF Soon after the MNA® was fi rst introduced, it was recognised that its complexity and length prevented its use as a screening tool Thus, the MNA ®SF (ShortForm) was developed by Rubenstein et al in 014 It is the fi rst 6 questions of the full MNA ®If an older person was identifi ed as at nutritional risk by these 6 questions (Screening score) then theMNASF), for the nutritional assessment of the participants We used the full MNA as the gold standard for nutritional assessment The full MNA scale has 18 items, provides a maximum possible overall assessment of 30 points and its nutritional categories are



Http Www Mna Elderly Com Publications 415 Pdf



An Evaluation Of The Validity Of Nutrition Screening And Assessment Tools In Patients Admitted To A Vascular Surgery Unit British Journal Of Nutrition Cambridge Core
The newly revised MNASF is a valid nutritional screening tool applicable to geriatric health care professionals with the option of using CC when BMI cannot be calculated This revised MNASF increases the applicability of this rapid screening tool in The MNASF is independently associated with 2 year mortality in dialysis patients It has a high negative predictive value for excluding being at risk or having malnutrition in the full score Therefore, it can be advocated as a screening tool for nutritional status in dialysis patientsSubjects If MNASF is normal (>10) there should be no need to complete a "full" MNA (14) A nurse's scoring of the MNASF was compared to an assessment of a clinical nutritionist, which was defined as the gold standard A study nurse performed the inception procedure and scored the MNASF The patients were weighted in a chair scale




Table 2 From The Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna After Years Of Research And Clinical Practice Semantic Scholar



Screening Of Nutritional Risk Among Older Persons
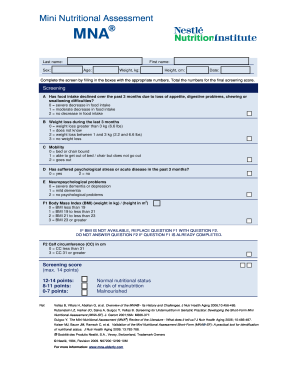
The MNASF is an interactive activity/questionnaire that is comprised of 6 items rated between 0 to 3 relative to aspects of subject's nutritional intake Scores can range from 0 to 14 with lower scores considered more problematicThe MiniNutritional Assessment ShortForm (MNASF) is a screening tool used to identify older adults (> 60 years) who are malnourished or at risk of malnutritionThe MNASF is based on the full MNA, the original Methods MUST and MNASF was performed on 78 patients (49 males and 29 females, age y ± 79, body mass index (BMI) 255 kg/m 2 ± 54), categorised by nutritional risk, and statistical comparison and test reliability performed BIA was performed in 66 patients and fat free mass (FFM), fat mass (FM) and body cell mass (BCM) and index values (kg/m 2) calculated



Predictive Value Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf And Nutritional Risk Screening Nrs02 In Hip Fracture European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




Figure 1 From The Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Review Of The Literature What Does It Tell Us Semantic Scholar
Mnasf Mini Nutritional Assessment short form Purpose The MNA® is a validated nutrition screening and assessment tool that can identify geriatric patients age 65 and above who are malnourished or at risk of malnutritionMNA® Video demonstrates stepbystep directions for using the MNA in clinical practice to identify malnutrition in the elderlyMore information on wwwmnael The MNASF has 6 questions instead of 18, eliminates timeconsuming and subjective items, and can be administered in approximately 3 minutes Whereas height and weight measurement do involve time and training, particularly with bedbound persons or amputees, these measures are relatively easy to obtain and are often available in patient records




Predictive Validity Of Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool Must And Short Form Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Sf In Terms Of Survival And Length Of Hospital Stay E Spen Journal



Www Nestlehealthscience In Sites G Files Dnigna226 Files Asset Library Documents Newsroom 4 Juergen Bauer Final Pdf
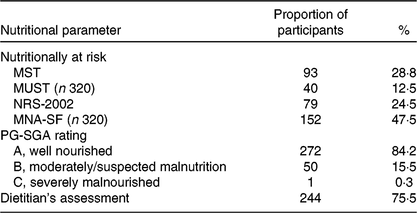
The MNASF showed that 1762 (646%) had normal nutritional status, 857 (314%) were at risk of malnutrition, and 107 (39%) were malnourished The NSI DETERMINE Checklist indicated that 1945 (696%) had good nutrition, 718 (257%) had moderate nutritional risk, and 131Get the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf you require Open it with online editor and start editing Fill out the empty areas; The NRS 02, MNAsf, and NRI are useful and practical tools with respect to screening for patients with COVID19 who are at nutritional risk,




Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Pdf Pdf4pro




The Role Of Early Nutrition Screening And Intervention In Lvad Therapy The Journal Of Heart And Lung Transplantation
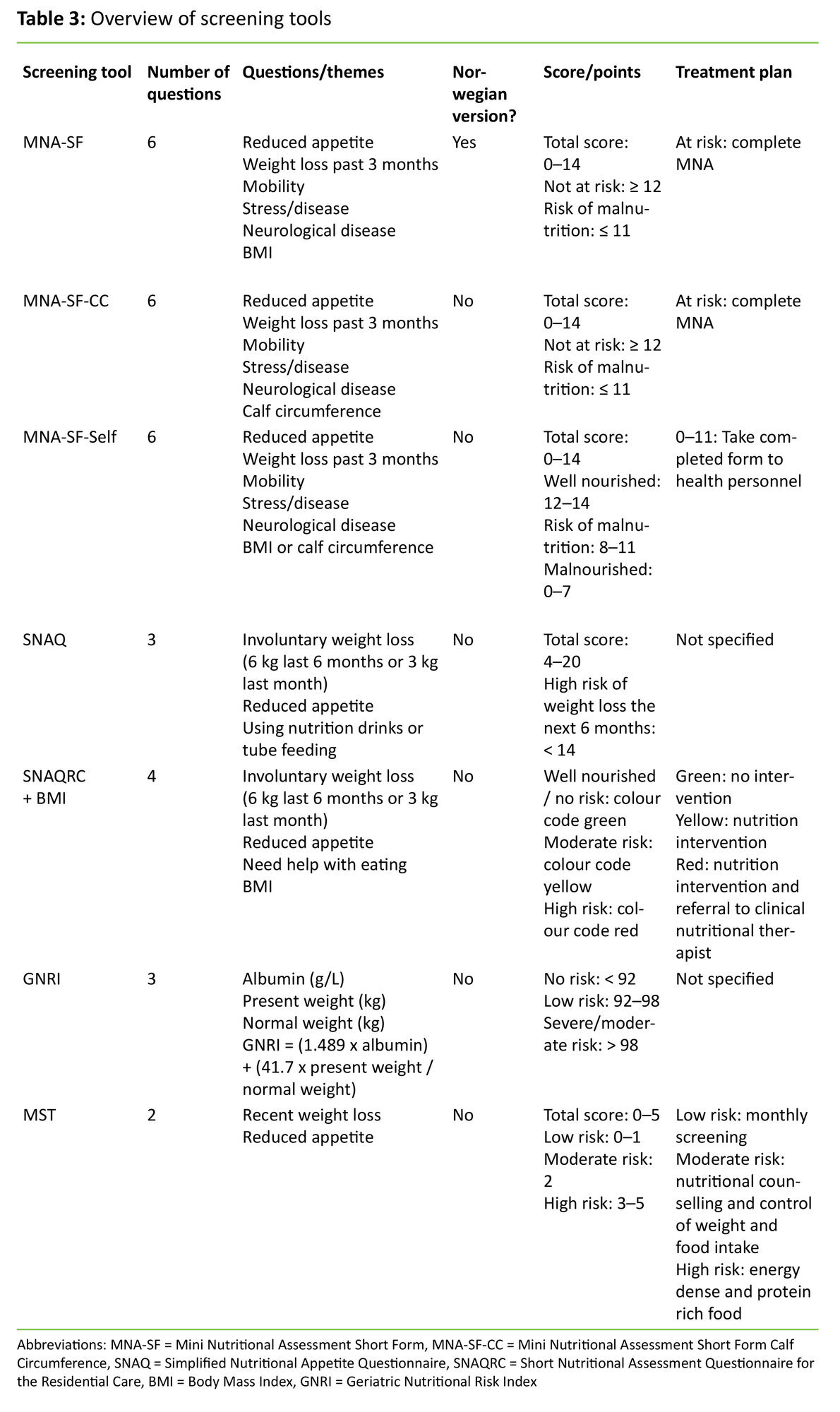
Six tools for identifying risk for malnutrition (undernutrition) with sufficient evidence for evaluation were selected Malnutrition Screening Tool (MST), Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool (MUST), Mini Nutrition Assessment – Short Form (MNASF), Short Nutritional Assessment Questionnaire (SNAQ), Mini Nutrition AssessmentShort FormBody Mass Index (MNASFBMI), and Nutrition The MNA®SF is a simple questionnaire of 6 items that can be completed in a shorter time than the MNA®, which consists of 18 items In addition, it is possible for care workers to evaluate the questionnaire Therefore, the evaluation of nutritional status using MNA®SF is less burdensome and might well predict deathThe MNASF is independently associated with 2 year mortality in dialysis patients It has a high negative predictive value for excluding being at risk or having malnutrition in the full score Therefore, it can be advocated as a screening tool for nutritional status in dialysis patients




Mna Sf



Mna Sf As A Screening Tool For Malnutrition Diagnosed With The Glim Criteria In Older Persons With Cancer Springerlink
To screen for malnutrition, we used the Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form (MNA SF) Results Fifty patients were included, median age 76 years (range 7087) Sixteen percent of the patients (n = 8) were malnourished and 66% (n = 33) were at riskIt also provides an opportunity for offering some kind of nutritional intervention, which in turn reduces hospital admission costs and improves the quality of life (Lozoya et al, 17) Next, discuss the predictive ability of the test(mnasf)2325 高齢者に使用する目的で具 体的かつ信頼性の高い、再 現可能な評価ツール。簡易 版(mnasf)はスクリー ニングツールとして使用 することができ、完全版 mnaはアセスメントツー ルになる。 食事歴、体重減少、bmi、




Mini Nutritional Assessment And Anthropometric Measurements Jmdh




The Relation Of Mini Nutritional Screening Score Subjective
According to the MNASF, only 73% of subjects had malnutrition, and 2% were at risk of malnutrition The agreement between the MNASF score and the GLIM criteria were observed in only 223% of the population The sensitivity and specificity of MNASF against the GLIM criteria were fair (592% and 7%, respectively)The MNA®SF is a screening tool to help identify elderly patients who are malnourished or at risk of malnutrition The User Guide will assist you in completing the MNA®SF accurately and consistently It explains each question and how to assign and interpret the score MNASF is a fast, simple, and sensitive method for screening both frailty and malnutrition Therefore, MNASF can easily be used for the older adults by clinicians to determine frailty status as well as nutritional status Thus, two geriatric syndromes, frailty and malnutrition, can be identified by MNASF simultaneously in geriatrics practice




Pdf Nutritional Screening Strategy In Nonagenarians The Value Of The Mna Sf Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form In Nutriaction Semantic Scholar



Plos One The Screening Score Of Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Is A Useful Routine Screening Tool For Malnutrition Risk In Patients On Maintenance Dialysis
Advantage of the MNASF is the identification of elderly individuals at nutritional risk before important weight changes could occur; The MNASF was more effective than the GNRI at predicting the development of POD, but the two nutrition screening methods have similar performance in predicting prolonged LOS among older noncardiac surgical patients Malnutrition has been shown to be associated with poor prognosis in older surgical patients Several tools are available forRESULTS MNASF classified 15% of the sample as malnourished and 41% as being at risk of malnutrition, whereas the MNALF classified 14% and 58%, respectively During the followup year, 15% of participants died




Agreement Between Mna Sf And Full Mna Download Table
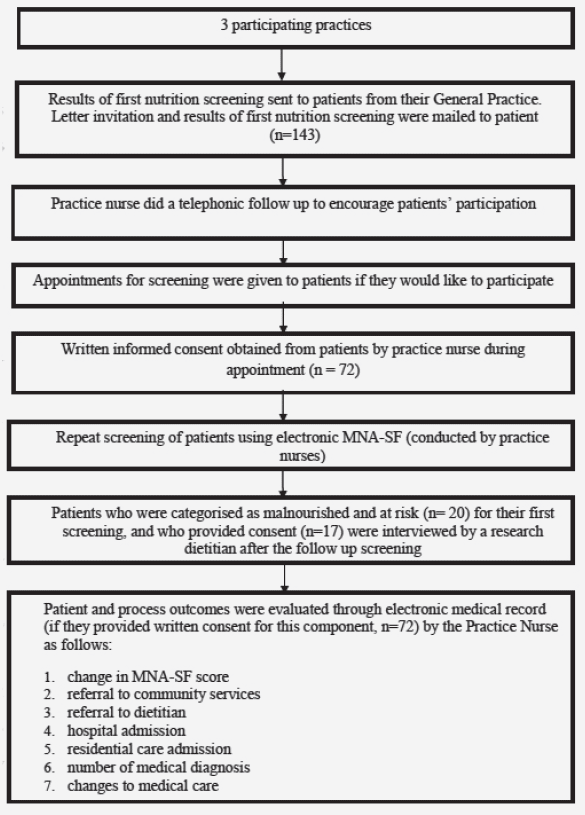



Implementation Of Nutrition Screening For Older Adults In General Practice Patient Perspectives Indicate Acceptability Jarlife
The MNASF includes only six items, but is quicker and as e ective as the long version If the total score is 11 points or less, the patient is considered at risk of malnutrition or malnourished and the full version (assessment) should be performed We examined the association of nutritional status as measured by the MiniNutritional Assessment Short Form (MNASF) with changes in mobility, institutionalization and MNASF is a validated nutritional screening scale and includes an ordinal scale ranging from 0 to 14 Scores of 0–7, 8–11, and 12–14 indicate malnutrition, risk of malnutrition, and normal nutritional status, respectively The MMSE represents global cognitive function, ranging from 0 (most severe) to 30 (normal)



Http Www Mna Elderly Com Publications 4 Pdf



Nutritional Assessment In Older Adults Mna 25 Years Of A Screening Tool A Reference Standard For Care And Research What Next Springerlink
According to the GLIM criteria, malnutrition affected 381% of patients with cirrhosis, being severe in 22% of the patients MNASF is the most accurate screening test, superior even to tools specifically designed for cirrhotic patients (LDUST)




Pdf Predictive Ability Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf In A Free Living Elderly Population A Cross Sectional Study Semantic Scholar



Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mna Guide English Sf Pdf
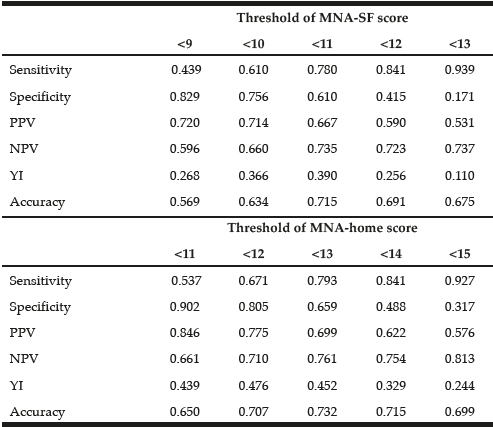



Modification Of The Mna Sf For Community Dwelling Older Adults At Risk Of Malnutrition Jarlife



Short Form Mini Nutritional Assessment As A Tool For Nutrition Evaluation In Elderly Individuals With Cancer In Brazil Jarlife



Plos One The Screening Score Of Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Is A Useful Routine Screening Tool For Malnutrition Risk In Patients On Maintenance Dialysis




Mini Nutritional Assessment Scale Short Form Can Be Useful For Frailty Cia



Http Www Hkcnaltd Org Hk Info Mna Pdf



Diversified Analysis Of Nutritional Status In Community Dwelling Older Adults In Japan Jarlife




The Validity Of Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf Questionnaire In Screening Malnutrition Among Elderly Aged 60 Years And Above In Urban Coimbatore Biostatistics



Www Researchsquare Com Article Rs V1 Pdf C




Evaluation Of Malnutrition Among Elderly People Living In Nursing Homes By Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf In Turkey Maedica A Journal Of Clinical Medicine




Association Between Mna Sf Nutritional Categories And Behavioural And Download Table



Www Nestlehealthscience In Sites G Files Dnigna226 Files Asset Library Documents Newsroom 4 Juergen Bauer Final Pdf



Frontiers Mini Nutritional Assessment Scores Indicate Higher Risk For Prospective Mortality And Contrasting Correlation With Age Related Epigenetic Biomarkers Endocrinology



Comparison Of Two Nutrition Assessment Tools In Surgical Elderly Inpatients In Northern China Nutrition Journal Full Text




Pdf Screening For Malnutrition In Elderly Acute Medical Patients The Usefulness Of Mna Sf Semantic Scholar




Uso Del Mini Nutritional Assessment Como Herramienta De Cribaje Nutricional En La Poblacion Mayor De 65 Anos En El Ambito Hospitalario Conveniencia Y Factibilidad
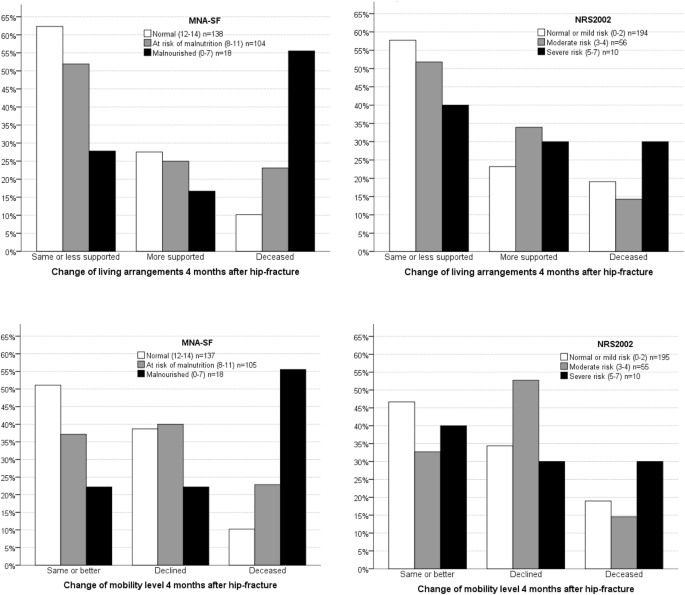



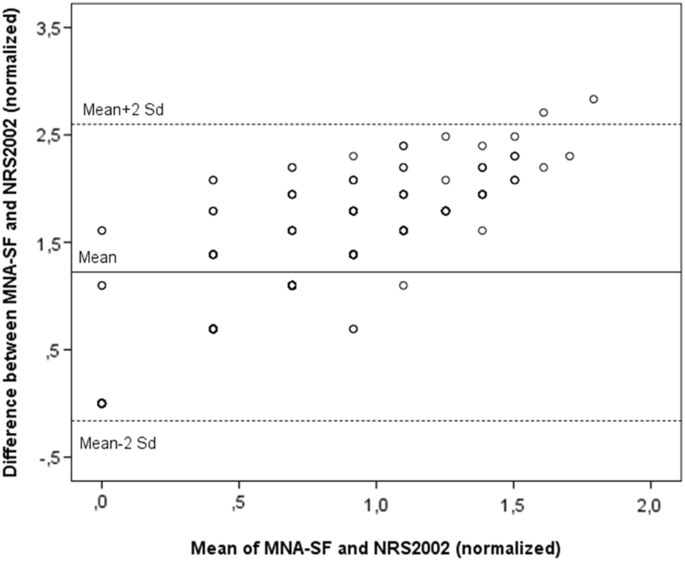
Predictive Value Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf And Nutritional Risk Screening Nrs02 In Hip Fracture European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




The Relation Of Mini Nutritional Screening Score Subjective




Evaluation Of The Efficacy Of Nutritional Screening Tools To Predict Malnutrition In The Elderly At A Geriatric Care Hospital Abstract Europe Pmc




Predictive Value Of Nutritional Risk Screening 02 And Mini Nutrition Cia



1




Table 2 From Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Without Body Mass Index Bmi Predicts Functional Disability In Elderly Taiwanese Semantic Scholar




Participants Characteristics And Functioning By Their Mna Sf Download Table




Nutritional Assessment In Older Adults Mna 25 Years Of A Screening Tool A Reference Standard For Care And Research What Next Springerlink
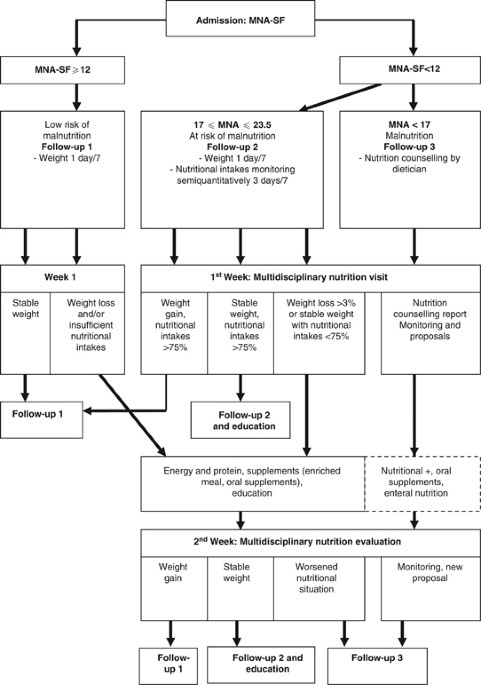



A Critical Pathway For The Management Of Elderly Inpatients With Malnutrition Effects On Serum Insulin Like Growth Factor I European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




Predictive Ability Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf In A Free Living Elderly Population A Cross Sectional Study Peerj



1



2




Analysis Of The Correlation Between Mna Mna Sf And Age Nutritional Download Table




Agreement Between Mna Sf And Full Mna Download Table




Supplemental Materials For A Comparison Of The Malnutrition Screening Tools Must Mna And Bioelectrical Impedance Assessment In Frail Older Hospital Patients Clinical Nutrition



Http Links Lww Com A366




Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Mna Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna ช อ สก ล




Malnutrition In The Elderly Underrecognized And Increasing In Prevalence Page 2 Of 3 Clinical Advisor




Evaluation Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf




Pdf Predictive Ability Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf In A Free Living Elderly Population A Cross Sectional Study Semantic Scholar



Mini Nutritional Assessment Fill Out And Sign Printable Pdf Template Signnow




Evaluation Of The Efficacy Of Nutritional Screening Tools To Predict Malnutrition In The Elderly At A Geriatric Care Hospital Abstract Europe Pmc



Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mna Guide Spanish Sf Pdf



Health Determinants Of Nutritional Status In Community Dwelling Older Population The Verisaude Study Public Health Nutrition Cambridge Core




Table 1 From Simplifications Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Are Predictive Of Mortality Among Hospitalized Young And Middle Aged Adults Semantic Scholar




Evaluacion Del Test Corto De Valoracion Nutricional Mna Sf En Ancianos Institucionalizados En Espana



Modification Of The Mna Sf For Community Dwelling Older Adults At Risk Of Malnutrition Jarlife




Nutrition Screening Mna Elderly



Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mna Guide English Sf Pdf




Agreement Between Mna Sf And Full Mna Download Table




Figure 3 From Validity Of The Self Mini Nutritional Assessment Self Mna For The Evaluation Of Nutritional Risk A Cross Sectional Study Conducted In General Practice Semantic Scholar



Figure 3 Ernahrungsmanagement In Der Alterstraumatologie Springerlink




Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Pdf Pdf4pro




The Components Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf Download Table



Nutritional Assessment In Older Adults Mna 25 Years Of A Screening Tool A Reference Standard For Care And Research What Next Springerlink



Http Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mini Mna Mini Portuguese Pdf




Identifying Geriatric Malnutrition In Nursing Practice The Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna An Evidence Based Screening Tool Journal Of Gerontological Nursing



A Critical Pathway For The Management Of Elderly Inpatients With Malnutrition Effects On Serum Insulin Like Growth Factor I European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition



Http Www Mna Elderly Com Mna Proceedings Pdf



Subjective Global Assessment
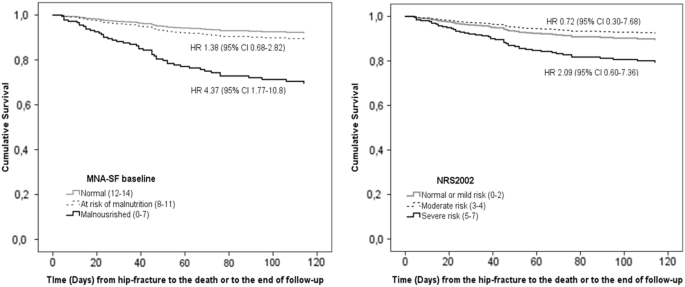



Predictive Value Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf And Nutritional Risk Screening Nrs02 In Hip Fracture European Journal Of Clinical Nutrition




Nestle Nutrition Institute Mna Elderly Mna Forms



The Screening Score Of Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna Is A Useful Routine Screening Tool For Malnutrition Risk In Patients On Maintenance Dialysis



Http Www Swrwoundcareprogram Ca Uploads Contentdocuments Hcpr mna procedure Pdf
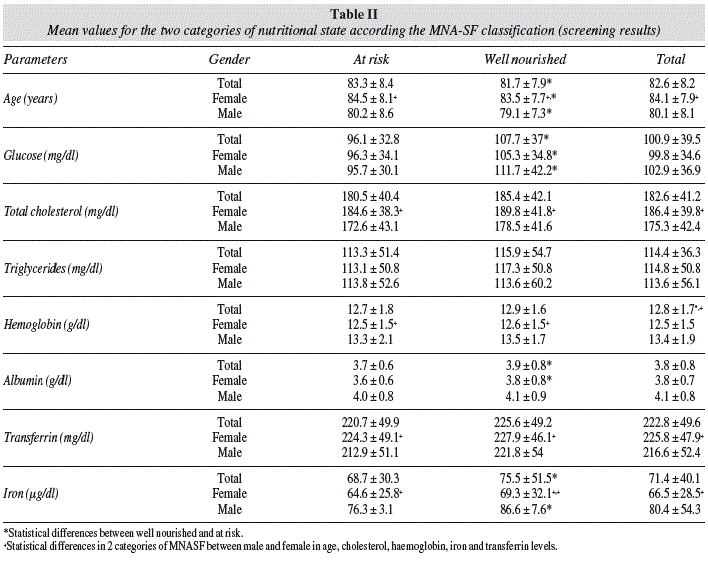



Evaluacion Del Test Corto De Valoracion Nutricional Mna Sf En Ancianos Institucionalizados En Espana




The Components Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Mna Sf Download Table



1




Full Form Nestle Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna C Nestle 1994 Download Scientific Diagram




Mini Nutritional Assessment And Anthropometric Measurements Jmdh




The Risk Of Dysphagia Is Associated With Malnutrition And Poor Functional Outcomes In A Large Population Of Outpatient Older Individuals Clinical Nutrition



Www Mpqhf Org Qio Wp Content Uploads 16 09 Nutrition 508 Compliant Pdf




Identifying Geriatric Malnutrition In Nursing Practice The Mini Nutritional Assessment Mna An Evidence Based Screening Tool Journal Of Gerontological Nursing




Pdf Nutritional Screening Strategy In Nonagenarians The Value Of The Mna Sf Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form In Nutriaction Semantic Scholar




The Nutritional Status Of Adult Female Patients With Disabilities In Kuwait Sciencedirect




Xmlinkhub




Acute Phase Nutritional Screening Tool Associated With Functional Outcomes Of Hip Fracture Patients A Longitudinal Study To Compare Mna Sf Must Nrs 02 And Gnri Clinical Nutrition



Www Mna Elderly Com Forms Mini Mna Mini Spanish Pdf



Plos One Screening And Application Of Nutritional Support In Elderly Hospitalized Patients Of A Tertiary Care Hospital In China




Mini Nutritional Assessment Scale Short Form Can Be Useful For Frailty Cia
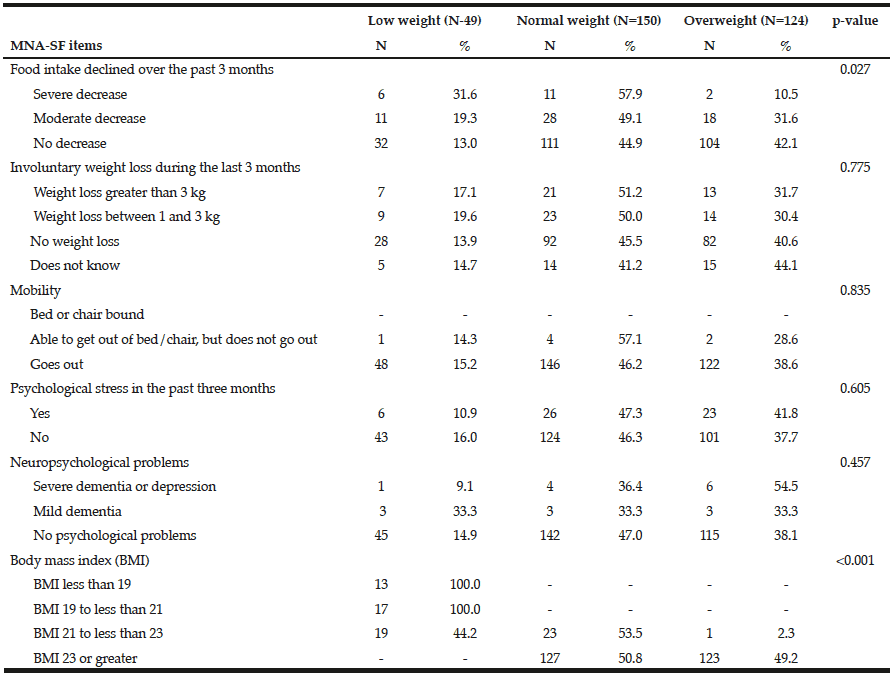



Short Form Mini Nutritional Assessment As A Tool For Nutrition Evaluation In Elderly Individuals With Cancer In Brazil Jarlife




Table 6 From Simplifications Of The Mini Nutritional Assessment Short Form Are Predictive Of Mortality Among Hospitalized Young And Middle Aged Adults Semantic Scholar


コメント
コメントを投稿